Introduction
In the modern digital world, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of seamless communication between software applications. Whether you’re browsing social media, checking the weather, or making an online purchase, APIs are working behind the scenes to make these interactions possible. This blog aims to demystify APIs for beginners by explaining their definition, functionality, types, and real-world applications.
What Is an API?
An API is a set of rules and protocols that allow different software components to communicate with each other. Think of it as a bridge or translator between two applications that enables them to exchange data or functionality without knowing how each is implemented internally.
For example, when you use a weather app on your phone, it retrieves real-time data from the weather bureau’s system via an API. The API acts as an intermediary, ensuring that your app receives accurate information in a format it can understand.
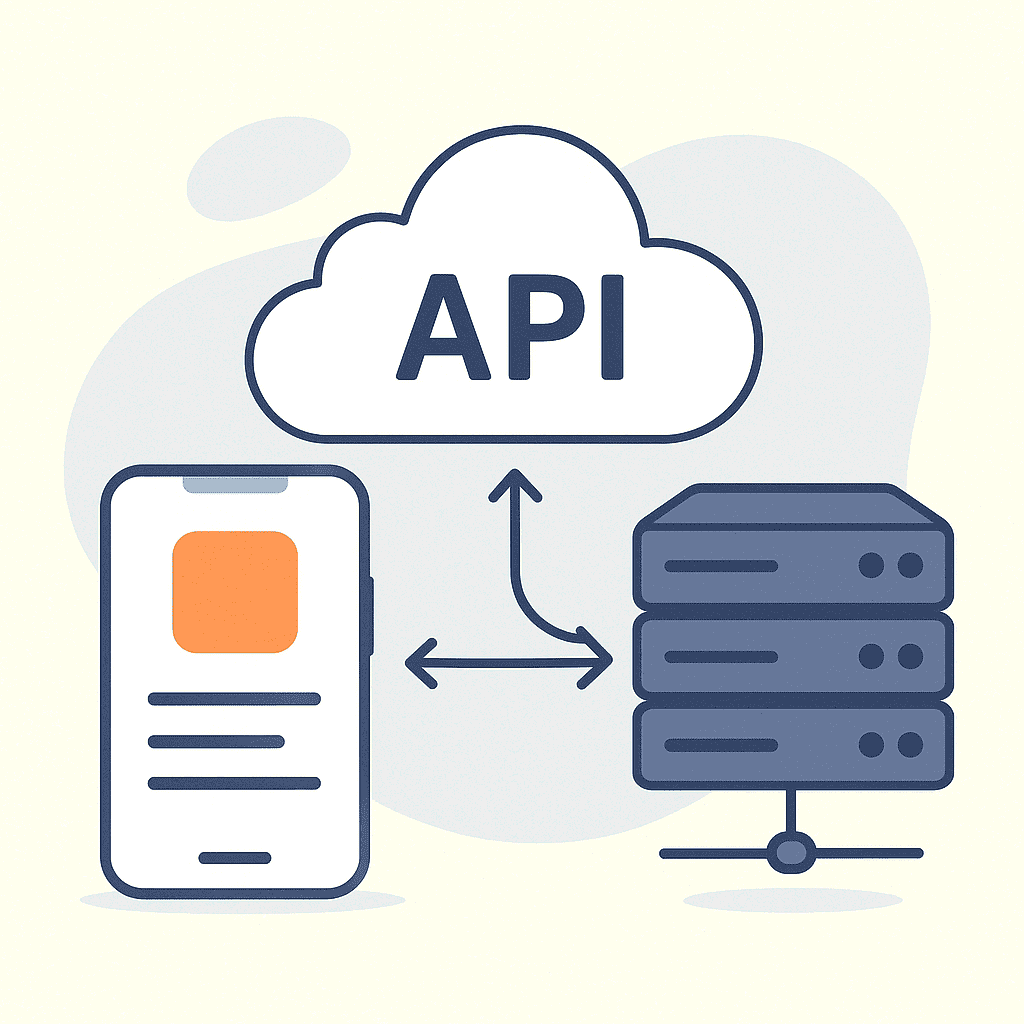
How Do APIs Work?
APIs operate through a request-response cycle:
- Client Request: The client application (e.g., your phone) sends a request to the server via the API.
- Server Response: The server processes the request and sends back the required data or functionality.
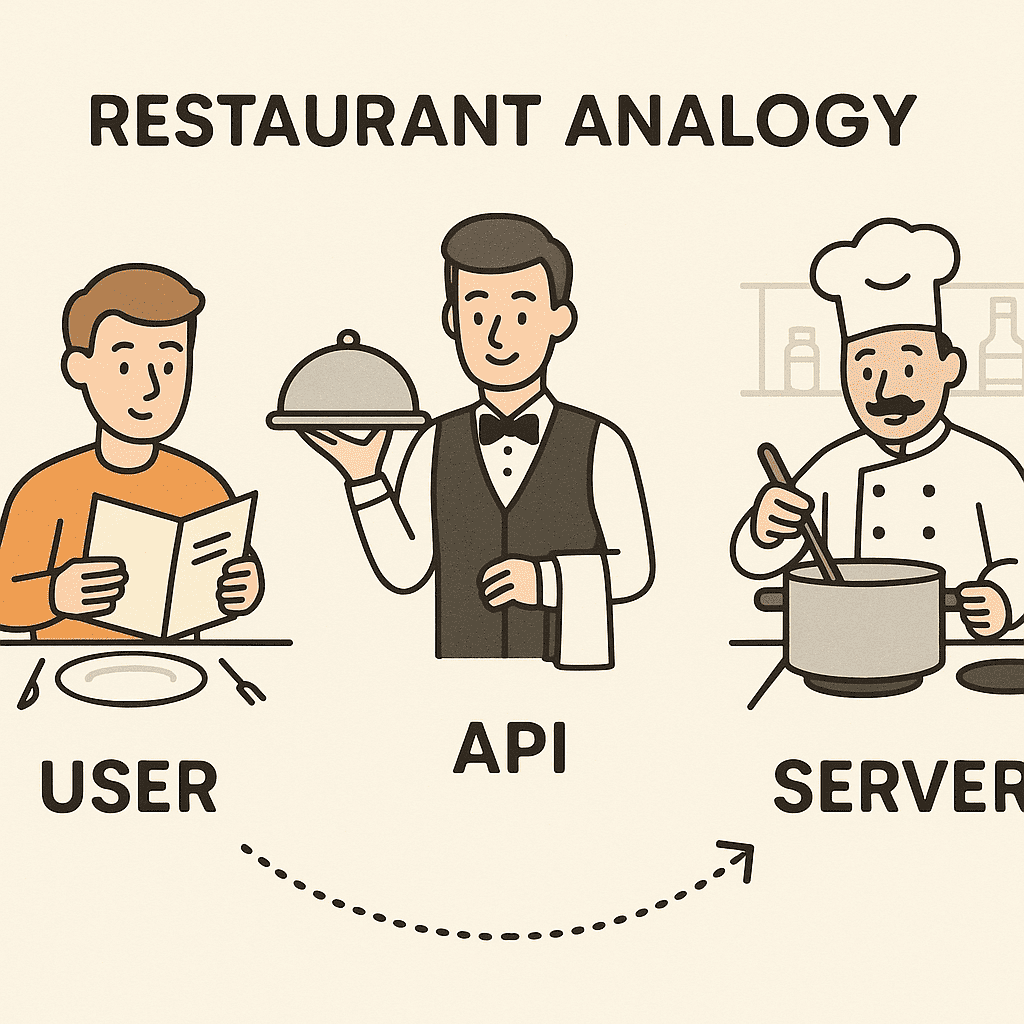
This interaction is often compared to ordering food at a restaurant: you (the client) place an order (request), and the kitchen (server) prepares your meal and delivers it via a waiter (API).
APIs can also work in event-driven architectures, where specific actions trigger API requests—for instance, receiving notifications after making a payment.
Types of APIs
APIs come in various types, tailored to different use cases:
- REST APIs: The most popular type today, REST APIs use HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to interact with resources. They are flexible and widely used for web services1.
- SOAP APIs: Older but reliable, SOAP APIs use XML for communication and are often employed in enterprise systems.
- Web-socket APIs: These enable real-time two-way communication between clients and servers, ideal for applications like chat platforms1.
- RPC APIs: Remote Procedure Call APIs allow clients to execute functions on servers and receive outputs.
Benefits of APIs
APIs offer numerous advantages:
- Efficiency: Developers can integrate existing functionalities instead of building them from scratch.
- Flexibility: APIs simplify application design and allow for easy updates or modifications.
- Security: By exposing only necessary data or functions, APIs help protect sensitive internal systems.
- Innovation: They enable businesses to create new services by combining functionalities from multiple sources.
Real-World Applications
APIs power countless everyday technologies:
- Social Media Integration: Platforms like Facebook and Twitter provide APIs for embedding feeds or sharing posts.
- Payment Gateways: Services like PayPal use APIs for secure online transactions.
- Maps and Navigation: Google Maps API allows developers to integrate location services into their apps.
- E-commerce: APIs connect inventory systems with online stores to display real-time stock availability.
Conclusion
APIs are fundamental tools that enable software applications to interact seamlessly. They simplify development processes, enhance security, and open doors to innovation. Whether you’re a beginner exploring programming or simply curious about technology, understanding APIs is key to appreciating how digital systems work together.
By learning about APIs, you gain insight into the invisible yet essential mechanisms that drive our interconnected world.
Table of Contents
Interesting Posts

Artist Portfolio HTML CSS Project

BSCS 5th Semester Notes

40+ Agency WordPress Template Kits FREE

More HTML

BSCS 2nd Semester Notes

HTML Forms
Ghulam Ahmad is an Excellent Writer, His magical words added value in growth of our life. Highly Recommended
- Irfan Ahmad Tweet








3 Responses