Introduction
HTTP status codes are integral to the functioning of the web, providing essential information about the interaction between a client (browser or API) and a server. These three-digit numbers serve as standardized responses that indicate whether a request was successful, redirected, or resulted in an error. This blog explores the different types of HTTP status codes, their significance, and practical applications.
What Are HTTP Status Codes?
HTTP status codes are generated by servers in response to requests made by clients. Managed by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), these codes adhere to standards set by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). They are categorized into five classes based on their first digit, with each class representing a distinct type of response:
- 1xx (Informational): Indicates that the server has received and is processing the request.
- 2xx (Success): Confirms that the request was successfully processed.
- 3xx (Redirection): Suggests further action is required to complete the request.
- 4xx (Client Error): Highlights issues originating from the client-side.
- 5xx (Server Error): Points to server-side failures preventing request fulfillment.
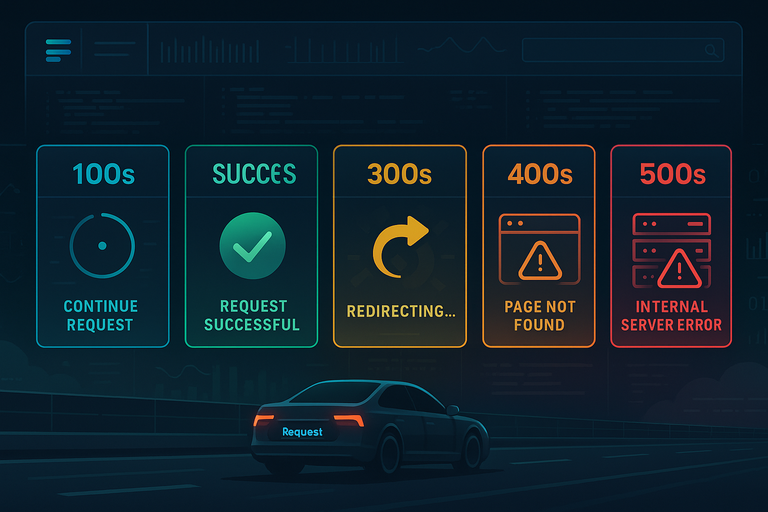
Detailed Breakdown of HTTP Status Code Classes
1xx – Informational Responses
These provisional codes signal that the server has received the request and is continuing processing.
- 100 Continue: The client can proceed with its request.
- 101 Switching Protocols: The server is switching protocols as requested by the client.
- 103 Early Hints: Provides preliminary information before a full response23.
2xx – Successful Responses
These codes confirm that the server successfully processed the request.
- 200 OK: The request was successful, and data is returned.
- 201 Created: A new resource has been created as a result of the request.
- 204 No Content: The request was successful, but there is no content to return23.
3xx – Redirection Responses
Redirection codes indicate that additional actions are needed.
- 301 Moved Permanently: The resource has been permanently relocated to a new URL.
- 302 Found: The resource resides temporarily at another location.
- 307 Temporary Redirect: Similar to 302 but ensures the method remains unchanged23.
4xx – Client Error Responses
These codes highlight errors caused by issues in the client’s request.
- 400 Bad Request: The server cannot process malformed syntax or invalid data.
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication is required for access.
- 403 Forbidden: Access to the resource is denied despite valid credentials.
- 404 Not Found: The requested resource does not exist on the server123.
5xx – Server Error Responses
Server-side errors prevent successful processing of valid requests.
Why Are HTTP Status Codes Important?
Understanding HTTP status codes is crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting Website Issues:
These codes help diagnose problems such as broken links (404 errors) or server overloads (503 errors), enabling quick fixes. - Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Search engines use status codes like 200 OK or 301 Moved Permanently to determine whether pages should be indexed or redirected correctly. - User Experience:
Proper handling of status codes ensures smooth navigation for users, minimizing frustration caused by errors like 403 Forbidden or 500 Internal Server Error. - Web Development and Monitoring:
Developers use tools like browser DevTools and Google Search Console to monitor HTTP responses for site optimization.
Conclusion
HTTP status codes are more than just numbers; they are vital communication tools between clients and servers. Whether you’re a developer troubleshooting errors, a marketer optimizing SEO, or simply curious about web technology, understanding these codes can empower you to navigate and manage digital ecosystems effectively. By mastering HTTP responses, you can ensure better performance, reliability, and user satisfaction for your web applications.
Table of Contents
Interesting Posts

BSCS 2nd Semester Notes

BSCS 8th Semester Notes
How to Deploy a Website Using GitHub Pages

The Box Model

Build a Full-Stack App with MERN Stack Pt 2

Hazel CV HTML CSS Project
Ghulam Ahmad is an Excellent Writer, His magical words added value in growth of our life. Highly Recommended
- Irfan Ahmad Tweet




3 Responses